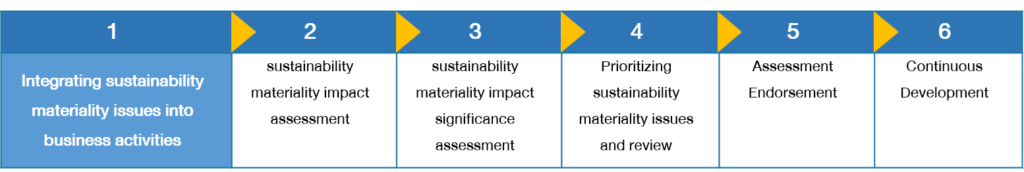
Materiality Assessment Procedure
OR materiality assessment considers the organization’s context, as well as the positive and negative impacts it has on the economy, environment, society, and all stakeholders. In addition, Materiality analysis is reviewed at least annually, and the assessment is conducted in accordance with the Global Reporting Initiative Standards (GRI Standards) framework and the principle of double materiality according to the following process:
1. Understand the Organization’s Context
OR has carefully considered the characteristics of its operations and the organizational context in which it conducts its downstream oil and retail businesses across the entire value chain and with its business relationship. This includes joint ventures with control, business partners and suppliers, oil dealers, and food and beverage franchisees, as well as all relevant stakeholders both within and outside the organization who may be affected by each activity.
The value chain diagram and related stakeholders can be found in the “Stakeholder Engagement” section.
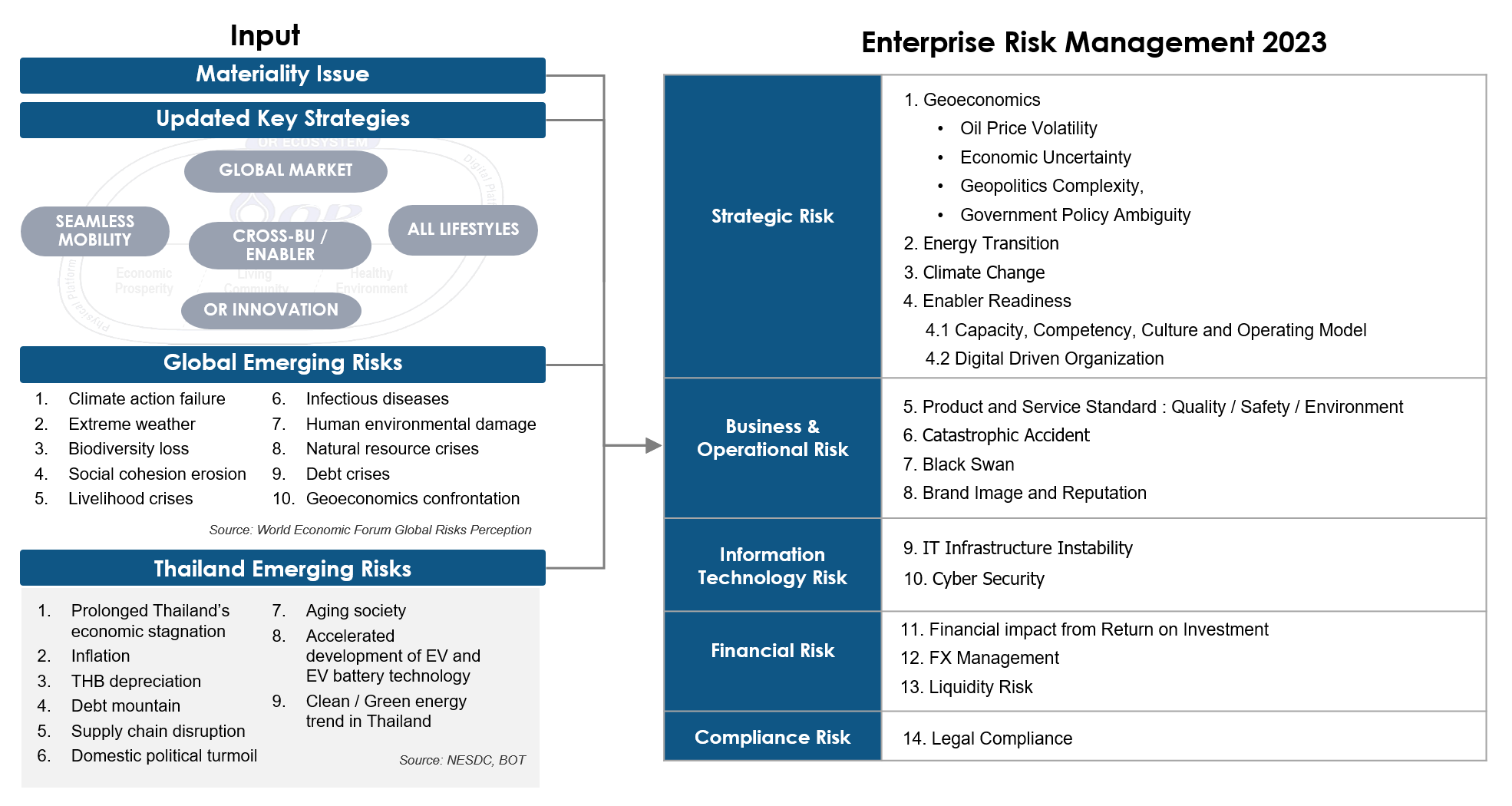
In the process of identifying and linking key sustainability issues, OR has taken a comprehensive approach that encompasses environmental, social, governance, and economic dimensions, while also considering human rights principles. Furthermore, OR has gathered key materiality issues from domestic and global sustainability trends of various standards and thought leaders such as the UN Global Compact (GCNT), UN Global Compact (UNGC), Morgan Stanley Capital International (MSCI), The World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD), World Economic Forum (WEF), and others. In addition, OR has considered the issues from peers (same sectors), both oil and retail businesses, are paying attention to, both globally, regionally and locally where OR operates.
Thought Leaders (2022) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  | |||||
Materiality Issue | GCNT – SDGs Mega rend 2022 (Corporate Climate Action) | Sustain Ability 2022 ESG Trend | MSCI ESG 2022 Trend | UNGC 10 Principles | WBCSD 2022 Principles | WBCSD Vision 2050 | WEF Global Risk Report 2022 |
Biodiversity | GCNT – SDGs Mega Trend 2022 (Corporate Climate Action) | Sustain Ability 2022 ESG Trend | MSCI ESG 2022 Trend | UNGC 10 Principles | WBCSD 2022 Projects | WBCSD Vision 2050 | WEF Global Risk Report 2022 |
Climate Change/ Climate Strategy | Nature-based Solutions | Safeguarding natural systems | Biodiversity and future of food | – | One Planet Business for Biodiversity | – | Biodiversity Loss |
Health and Well-being | – | Responding to climate change | Net-Zero target, Net-Zero Supply Chain | – | Natural Climate Solutions | – | – |
“Integrating ESG | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
(Investment strategies, ESG products etc.)” | SOS 1.5 (Climate target)” | – | Climate Action Failure | – | – | – | – |
Policy Influence | – | – | Global health crisis, COVID-19, investment in antibiotics | – | Health and Well-being | Health and Well-being | Infectious Disease |
Human Rights | – | Integrating ESG | Rethinking Divestment, Net-zero portfolio, engage in policy discussion | Principle 9 | – | – | – |
Digital transformation/ Digitalization | – | Shaping policy, regulations and norms | Rethinking Divestment, Net-zero portfolio, engage in policy discussion | – | Policy and Financing | – | – |
Environmental Management | Human Rights | Protecting of fundamental rights | – | Principle 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 | – | – | – |
2. Assess the Significance of the Impacts
OR gathers stakeholder feedback on materiality issues from the perspective of Impact Materiality and Financial Materiality in step 2. By calculating the level of positive and negative impact from the feedback obtained from the interviews, consider the level of severity which covers Scale, scope of impact, and irremediability and the likelihood of impact. The evaluation criteria are defined as 4 levels (critical, high, medium, and low) based on the severity that will occur, using the Impact Matrix that references the Enterprise Risk Matrix to identify the Impact Level.
3. Prioritize the Most Significant Impacts
OR prioritizes materiality issues using a two-dimension approach according to the assessment conducted based on the principle of double materiality .To effectively manage these issues, OR has established a three-tiered prioritization system: Fundamental, Strengthen, and Value Creation. This framework guides OR’s efforts in addressing sustainability concerns, ensuring that the most critical issues receive the necessary attention and resources. The entire process involves consulting sustainability experts from external agencies who analyze and assess the alignment of the importance ranking with relevant OR departments. Additionally, the material topics are tested with experts and information users.
4. Assessment Endorsement
OR’s Sustainability and Business Cooperation Executive Committee reviews and approves the results of OR’s sustainability risk and opportunity assessment. This assessment considers the impact of sustainability issues on OR’s stakeholders in the areas of economics, environment, society, and human rights. The committee is responsible for setting OR’s corporate sustainability strategy and goals. It also approves the scope of disclosure of sustainability materiality issues in the 2023 Sustainability Report and presents the materiality assessment results to the Corporate Governance and Sustainability Committee (Board of Directors) for final endorsement and signed off. Furthermore, Materiality issues are identified through a materiality assessment process that is integrated into OR’s enterprise risk management (ERM) process. These issues are also considered as inputs into the planning and development of OR’s strategies and initiatives.
5. Continuous Development
OR has developed materiality assessment process based on the principles of the GRI Standards to ensure that its sustainability assessment and reporting is comprehensive. This process is carried out in conjunction with the development of the annual sustainability report, and the materiality assessment process is verified by a third-party assurance provider. In addition, OR analyzes areas for continuous improvement, which are then integrated with the feedback from all stakeholders. This feedback is used to improve OR’s operations and sustainability reporting.
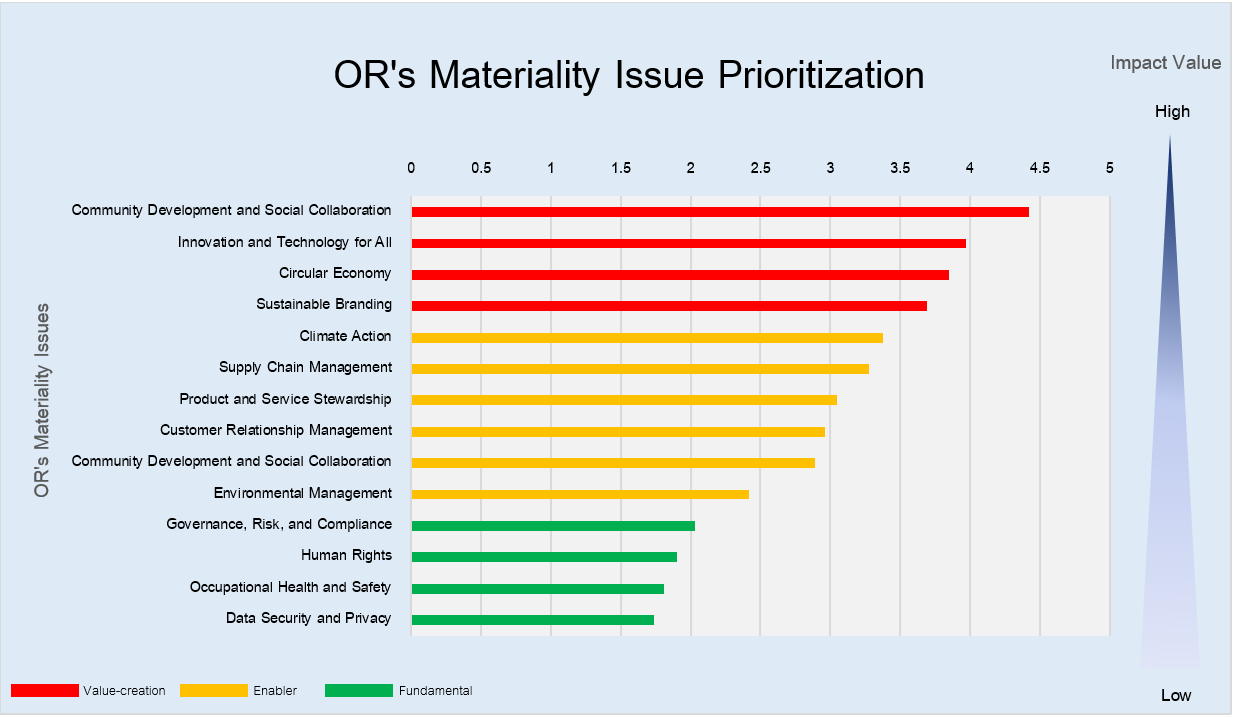
OR Materiality Assessment Results
OR’s materiality assessment, conducted in accordance with the GRI Standards, considers the company’s business operations, stakeholder expectations and impacts, and global sustainability trends. The assessment identified 16 key sustainability issues for 2023, two of which are new compared to 2022: stakeholder engagement and biodiversity. These issues have gained increasing attention from stakeholders. OR has also refined the details and names of other key issues to align them more clearly with stakeholder expectations and the company’s business strategy.
The materiality issues for OR in 2023, as summarized from the above process, are as follows:
Impact Value | Key Content to consider | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
3.68 – 5.00 | Value Creation | Materiality issues that create value or pose high risks, with the key issues classified at this level, are those that can either create value for OR’s stakeholders and business, or pose risks to OR’s stakeholders and business. Value Creation may involve generating good operational results, achieving high profits, and fostering business growth, while high risks may result in significant expenses, losses, or damage to the business. This level requires OR to establish clear objectives, action plans, and reports on operations results. | • Establishing organizational Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and using them as input for strategy development and various initiatives.
• Setting long-term targets and reporting progress in operation • Defining management approaches • Collecting data for at least 3 years and verifying it through third-party validation. • Presenting outstanding operational highlight case. | |
2.34 – 3.67 | Strengthen | Materiality issues that promote value creation/risk management, with key issues identified at this level considered to enhance the organization’s resilience and drive value creation for stakeholders and OR’s business, are areas where OR should develop improvement plans or consider as significant. These areas can help create value or mitigate risks. | • Establish organization metrics and incorporate them as factors in strategy development or various initiatives.
• Set long-term targets and report progress in operations. • Define management approaches • Collect data for at least 3 years and verify it with a third party. | |
1.00 – 2.33 | Fundamental | Materiality issues that are fundamental must be managed according to regulations, requirements, and laws, including normal standards/practices, are essential for OR’s business operations. This level represents the basic level that OR should maintain, monitor, and vigilantly ensure there are no violations or outcomes below industry peer standards. | • Establishing a management approach according to the business as usual model
• Collecting data according to the specified indicators. | |
Definitions | Priority | Value Chain | Stakeholder | Effect (Positive/Negative) | Impact Materiality and Importance to Society and Environment | SDGs | GRI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Economic Aspect | |||||||
1. Governance, Risk and Compliance: GRC (GRI 2, 205, 415)
• Corporate Governance • Business Ethics, Code of Conduct and Corporate Compliance • Risk and Crisis Management • Tax Strategy • Economic Performance | Conducting business operations with transparent systems or processes and ethical conduct ensures that the company can oversee and manage its operations to meet the needs of stakeholders appropriately and in compliance with relevant regulations, laws, and standards. This applies across economic, social, and environmental aspects, as well as having mechanisms for risk management, crisis situations, and operations under abnormal conditions. This also includes preparing to cope with leading the business through various situations effectively. | Fundamental | • Procurement of raw materials
• Transportation • Product and services • Delivery of products and services • Supporting activities | • This is a fundamental issue that the company must address. If there are good practices, stakeholders will gain confidence and trust.
• It affects the management of other risks that impact performance and the positive image of the organization. | Country/
Shareholders/Investors
Business Partner and Suppliers
Society and Community
Customers
Employees
|  | GRI 2
GRI 205
GRI 415 |
2. Supply Chain Management | Managing the supply chain through fair partner selection, monitoring, and assessing partner risks, as well as establishing measures to mitigate risks, may occur in the supply chain. This enables partners to efficiently fulfill responsibilities throughout the supply chain, both in normal and unexpected situations, and promotes sustainable business operations in economic, social, and environmental aspects. | Fundamental | • Procurement of raw materials
• Transportation • Product and services • Delivery of products and services • Supporting activities | • Increase efficiency in production by reducing costs, leading to increased profits.
• Promote the development of partners’ capabilities in quality, service, and sustainability practices. • Promote transparency in partner management practices. • Inefficient supply chain management leads to poor quality control and substandard manufacturing processes. | Country/
Shareholders/Investors
Business Partner and Suppliers
Society and Community |  | GRI 2
GRI 308
GRI 414 |
3. Customer Relationship Management | Managing customer relationships by fostering rapport and ensuring customer satisfaction through delivering positive experiences, including customer service that meets their needs. This ensures customers receive quality, safe products and services, fulfilling expectations and instilling confidence in choosing the company’s products and services. | Strengthen | • Delivery of products and services
• Supporting activities | • Building confidence in providing excellent service to customers and consumers.
• Stimulating sales and increasing revenue for dealers | Country
Shareholders/Investors
Customers
Employees
|  | GRI 418 |
4. Product and Service Stewardship
• Quality Products and Services • Product Stewardship • Health and Wellbeing Promotion Products | Ensuring the quality and safety of products and services in compliance with laws, regulations, international standards, and stakeholder expectations to assure that the company’s products and services do not negatively impact society and the environment. This also encompasses supporting products that promote health and well-being in society. | Fundamental | • Procurement of raw materials
• Product and services • Delivery of products and services • Supporting activities | • Promoting the enhancement of quality and safety of products and services
• The impact of using products and services on the environment and society. | Country
Society and Community
Customers
Employees
Shareholders/Investors
|  | GRI 416
GRI 417 |
5. Innovation and Technology for All
• Digitalization • ESG Investment and Market Opportunities | Meeting Stakeholders’ Expectations through Technology and Digital Systems’ Involvement in Product and Service Development to Add Value, Addressing Present and Future Changes, and Internal Innovation to Enhance Operational Efficiency, Elevating the Organization’s Competitive Edge. | Fundamental | • Procurement of raw materials
• Transportation • Product and services • Delivery of products and services • Supporting activities | • Delivering Value-Added Products and Services to Meet the Diverse Needs of Stakeholders.
• Convenience in Employee Operations. • Opportunities for innovation and technology development in collaboration with SMEs. | Country
Shareholders/Investors
Business Partner and Suppliers
Society and Community
Customers
Employees |  | – |
6. Data Security and Privacy
• Cybersecurity Governance • Cybersecurity and Cybersecurity and System Availability | Maintaining data security by implementing systems to prevent incidents related to data security and/or cybersecurity, including responding to and managing serious security incidents (such as data theft of sensitive organizational information through cyber means), appropriately. Additionally, emphasizing the importance of privacy data and building confidence in safeguarding personal data of stakeholders both within and outside the organization. | Fundamental | • Supporting activities | • Financial losses occur when addressing issues and operations come to a halt.
• Leads to a loss of trust and confidence from stakeholders. • Confidence of stakeholders in the organization. | Country
Shareholders/Investors
Business Partner and Suppliers
Society and Community
Customers
Employees |  | GRI 418 |
Social Aspect | |||||||
7. Human Rights
• Labour Practices • Diversity and Equal Opportunity and Inclusivity | Respecting labor rights according to international human rights principles, and establishing policies and business operations dedicated to respecting and protecting human rights, as well as avoiding causing adverse human rights impacts through business activities. This includes considering the rights of workers that employees of the organization should receive appropriately, such as wages, salaries, diversity, and equality through creating a work environment and organizational culture that fosters a sense of belonging, embraces diversity, promotes mutual respect, and does not discriminate based on differences in age, gender, sexual orientation, religion, disability, education, or nationality. | Fundamental | • Procurement of raw materials
• Transportation • Product and services • Delivery of products and services • Supporting activities | • Violations of human rights of stakeholders within the supply chain can significantly impact the confidence and reputation of the organization in the eyes of those stakeholders.
• Promoting equality in society through the operations of the organization. | Country
Shareholders/Investors
Business Partner and Suppliers
Society and Community
Customers
Employees
|  | GRI 2
GRI 406
GRI 408
GRI 409
GRI 410
GRI 411
GRI 414 |
8. Workforce Development & Well-Being
• Human Capital Development • Talent Attraction and Retention • Employee Health and Well-Being | The development of human resources to align with business strategies and enhance efficiency in the workplace through employee development initiatives, such as training and supporting employee education expenses, as well as implementing tracking and evaluation systems that reflect the return on investment in human resource development. Additionally, it encompasses efforts to retain employees and reduce turnover rates through fostering inclusivity, providing advancement opportunities, and ensuring occupational stability, as well as offering appropriate benefits and rewards that promote employee well-being and satisfaction. | Strengthen | • Procurement of raw materials
• Transportation • Product and services • Delivery of products and services • Supporting activities | • Enhancing employees’ skills and abilities leads to increased productivity in production. It fosters progress and builds career stability.
• Employee efficiency at work has decreased, and the resignation rate has increased. • There is a risk of producing outdated products and services, which affects consumer or service user satisfaction. | Country
Shareholders/Investors
Business Partner and Suppliers
Customers
Employees |  | GRI 2
GRI 201
GRI 401
GRI 405 |
9. Occupational Health and Safety | Occupational Health and Safety management that covers the safety of the company personnel and contractors working for the organization. This is under a good safety policy and management system which will help reduce and control the risks that may arise from operations. This is to ensure that the company can operate its business continuously without emergency incidents such as oil and chemical spills, transportation accidents, and epidemics. This leads to interruption of operations. Loss of life, property, and organizational reputation including impacts on the environment and community. | Fundamental | • Procurement of raw materials
• Transportation • Product and services • Delivery of products and services • Supporting activities | • Ensuring the safety of both lives and property of those involved.
• Promoting the creation of a safe environment and society from both normal and abnormal events. • Continuity in business operations. • Building trust among stakeholders and establishing a good reputation for the organization. | Country
Shareholders/Investors
Business Partner and Suppliers
Society and Community
Customers
Employees |  | GRI 403 |
10. Community Development and Social Collaboration
• Corporate Citizenship & Community Development • Community Investment, Engagement and Development, Social Contribution • Local/ Business Partnership | Business operations are intertwined with creating value for the community and society through activities or projects that benefit them economically, socially, and environmentally. This fosters community trust in the organization. Additionally, it entails being a responsible citizen by conducting business in alignment with the sustainable development goals (SDGs) set by the United Nations, promoting sustainable development. | Value – creation | • Procurement of raw materials
• Transportation • Product and services • Delivery of products and services • Supporting activities | • Minimize the risk of generating adverse impacts from business operations on the environment, communities, and society.
• Opportunities to integrate social activities into every process of the organization (CSR in Process). • Sourcing raw materials or supporting local community activities can help develop skills and increase income opportunities for the community. | Country
Shareholders/Investors
Business Partner and Suppliers
Society and Community
Customers
Employees
|  | GRI 201
GRI 413 |
11. Sustainable Branding
• Branding Management • Social License to Operate • Wealth Distribution • Collaborativeness | Operating the business according to the organization’s vision and mission to establish a sustainable organizational image through ethical practices, community and societal acceptance, and meeting stakeholder expectations. This involves focusing on collaboration with various sectors and promoting income distribution to localities, ensuring confidence that the company can grow sustainably alongside the community. | Value – creation | • Procurement of raw materials
• Transportation • Product and services • Delivery of products and services • Supporting activities | • The confidence of stakeholders.
• Collaboration in executing various projects together with stakeholders, both internal and external • A positive image impacts shareholders and stakeholders as the Brand Carrier of the PTT Group. | Country
Shareholders/Investors
Business Partner and Suppliers
Society and Community
Customers
Employees |  | GRI 417 |
12. Stakeholder Capitalism
• Stakeholder Management • Stakeholder Engagement | Ensuring the continuous improvement of business operations to meet the expectations of all stakeholders, both internal and external, involves developing strategies for stakeholder engagement based on their interests and expectations. This includes appointing efficient managers responsible for stakeholder relations, consistently monitoring collaborative efforts, and incorporating stakeholder feedback to align management practices with their needs effectively. By doing so, the organization can mitigate risks, foster confidence, build strong relationships, and establish long-term commitment with stakeholders. | Strengthen | • Procurement of raw materials
• Product and services | • Improving business efficiency and better meeting stakeholder expectations.
• Leading to a better understanding of business context and the ability to respond effectively to stakeholders’ needs. • Impacting expectations and potentially leading to future conflicts. | Country
Shareholders/Investors
Business Partner and Suppliers
Society and Community
Customers
Employees |  | GRI 301
GRI 306 |
Environmental Aspect | |||||||
13. Climate Action
• Climate Strategy and Target • Climate Governance | Prioritizing climate change management throughout the company’s operations and supply chains, including direct and indirect impacts, and assessing risks and opportunities to effectively plan for climate change. This involves addressing both physical risks and transitional risks that may impact the company. Additionally, reporting greenhouse gas emissions data to identify significant sources and causes, leading to management efforts to reduce emissions. The goal is for the organization to achieve carbon neutrality by 2030 and net-zero emissions by 2050. Furthermore, it involves fostering collaboration to support efforts to address climate change at both national and global levels. | Value Creation | • Procurement of raw materials
• Transportation • Product and services • Delivery of products and services • Supporting activities | • Supporting the use of alternative energy and installing electric vehicle charging stations can drive compliance with government policies aimed at achieving net-zero greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, it meets the increasing demand from customers.
• This impacts business opportunities and stakeholders’ expectations due to investors’ emphasis on it as a critical issue. | Country
Shareholders/Investors
Business Partner and Suppliers
Society and Community
Customers
Employees |  | GRI 305 |
14. Circular Economy
• Packaging and Plastic Management • Environmental Management & Policy • Operational Eco Efficiency • Water Management • Air Quality Management • Food Loss & Food Waste | Establishing environmentally friendly policies and implementing efficient and standardized environmental management systems is crucial. This includes processes for preventing and mitigating impacts, such as controlling pollution release into the environment, particularly from transportation and service provision. Additionally, it encompasses efforts to reduce food waste and manage food waste generated from operations. | Strengthen | • Procurement of raw materials
• Transportation • Product and services • Delivery of products and services • Supporting activities | • Reducing environmental impacts from business operations on stakeholders both internally and externally.
• Opportunities to seek efficient environmental management technologies and reduce resource waste. • Leading to non-compliance with environmental regulations and standards. | Country
Shareholders/Investors
Business Partner and Suppliers
Society and Community
Customers
Employees |  | GRI 303
GRI 304
GRI 306
GRI 307 |
- Value Creation – Materiality issues that create value or pose high risks, with the key issues classified at this level, are those that can either create value for OR’s stakeholders and business, or pose risks to OR’s stakeholders and business. Value Creation may involve generating good operational results, achieving high profits, and fostering business growth, while high risks may result in significant expenses, losses, or damage to the business. This level requires OR to establish clear objectives, action plans, and reports on operations results. OR
- Strengthen – Materiality issues that promote value creation/risk management, with key issues identified at this level considered to enhance the organization’s resilience and drive value creation for stakeholders and OR’s business, are areas where OR should develop improvement plans or consider as significant. These areas can help create value or mitigate risks.
- Fundamental – Materiality issues that are fundamental must be managed according to regulations, requirements, and laws, including normal standards/practices, are essential for OR’s business operations. This level represents the basic level that OR should maintain, monitor, and vigilantly ensure there are no violations or outcomes below industry peer standards.